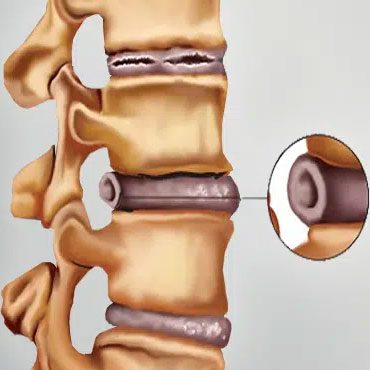
Disc Bulge
A disc bulge, also known as bulging disc or protruding disc, refers to the condition where the outer layer of a spinal disc slightly expands beyond its normal boundary but does not rupture. This can lead to pressure on surrounding nerves, causing pain, numbness, or other symptoms.
Causes of Disc Bulge
- Age-Related Degeneration: With age, spinal discs lose water content, making them more prone to bulging.
- Repetitive Stress: Repeated movements, poor posture, or heavy lifting can strain the discs.
- Trauma or Injury: Accidents, falls, or sudden impact injuries can lead to disc bulging.
- Poor Posture: Prolonged poor posture puts stress on the spine, leading to disc problems.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases pressure on spinal discs, contributing to bulging.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to weaker discs.
Symptoms of Disc Bulge
- Mild to Moderate Pain: Pain may occur in the lower back, neck, or other areas where the bulging disc presses on nearby nerves.
- Numbness/Tingling: Tingling or "pins and needles" sensations in the arms, legs, or hands.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles controlled by the affected nerves.
- Reduced Flexibility: Difficulty bending, twisting, or turning without discomfort.
